|
UMI-2000 Coal GAC 400 Activated Carbon
What are two types of Activated Carbon? Two types of Activated Carbon are Re-Agglomerated Coal based Activated Carbon manufactured
in the USA and Direct Activated "Crud" Carbon from Off-Shore (Asia). Re-Agglomerated Activated Carbon has up to 3 times the
Adsorptive Capacity of Direct Activated Carbon. Activated carbon treatment is the most studied treatment for PFAS removal.
Activated carbon is commonly used to adsorb natural organic compounds, taste and odor compounds, and synthetic organic chemicals
in drinking water treatment systems. Adsorption is both the physical and chemical process of accumulating a substance, such
as PFAS, at the interface between liquid and solids phases. Activated carbon is an effective adsorbent because it is a highly
porous material and provides a large surface area to which contaminants may adsorb. Activated Carbon is made from organic
materials with high carbon contents such as bituminous coal, lignite coal, virgin coconut shells and is often used in granular
form called granular activated carbon (GAC). This highly porous carbonaceous material has been shown to effectively remove
PFAS and other organic contaminants from drinking water when it is used in a flow through filter mode after particulates have
already been removed. EPA researcher Thomas Speth says GAC can be 100 percent effective for a period of time, depending on
the type of carbon used, the depth of the bed of carbon, flow rate of the water, the specific PFAS needed to be removed, temperature,
and the degree and type of organic matter as well as other contaminants, or constituents, in the water. For example, GAC works
well on longer-chain PFAS compounds like PFOA and PFOS.

REMOVAL OF PFAS FROM GROUND AND SURFACE WATER with Granular Activated Carbon. Our top activated carbon made in the USA is
COAL GAC 400 RE-AGGLOMERATED GRANULAR ACTIVATED CARBON. DEMONSTRATES SUPERIOR ADSORPTION OF PFAS Compounds PFOA and PFOS from
water.
Benefits: Enables the removal of PFOA and PFOS from ground and surface water to non-detectable levels and well below the 70
PPT advisory level set by the EPA. Resists interference from Total Organic Carbon (TOC) for enhanced performance. Coal GAC
400 demonstrates much higher performance when compared to coconut-based GAC and direct activated coal based carbons commonly
referred to as "Crud Carbons". Coal GAC 400 lowers operating costs by enabling the treatment of more bed volumes of water
before change-out of spent Activated Carbon. PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and PFOS (perfluoro-octane sulfonate), also known
as Poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances or PFAS, are man-made substances used in products such as non-stick cookware, waxy
food package coatings, water resistant clothing, stain resistant carpets and fabrics, and aqueous fire-fighting foams (AFFF).
Once in the environment, these chemicals are persistent, toxic, bio-accumulative, bio-transformative, and pose risks to human
health. In May 2016, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established a human Health Advisory Limit (HAL)
of 70 ppt for the combined exposure concentration of PFOA and PFOS in drinking water.
When compared to direct activated "CocoCrud" coconut shell based carbons in surface and ground waters, actual third party
case studies and our tests found that Coal GAC 400 activated carbon demonstrated superior performance in the removal of PFAS
compounds. Unlike other types of granulated activated carbon (GAC), our Coal GAC 400 resisted interference from Total Organic
Carbon (TOC) that reduce the carbon adsorptive capacity for contaminants like PFOA and PFOS. In other studies involving groundwater
with low TOC, the performance of our activated carbon was also superior to other direct activated coal-based carbons and surpassed
direct activated coconut shell based carbon.

United Manufacturing International 2000 Re-Agglomerated Coal GAC 400 is a granular activated carbon for the removal of dissolved
organic compounds from water and wastewater as well as industrial and food processing streams. These contaminants include
taste and odor compounds, organic color, total organic carbon (TOC), industrial organic compounds such as TCE and PCE, and
PFAS. This Activated Carbon is made from select grades of bituminous coal through a process known as re-agglomeration to produce
a high activity, durable, granular product capable of withstanding the abrasion associated with repeated back-washing, hydraulic
transport, and reactivation for reuse. The raw coal is mined and subsequently manufactured into Granular Activated Carbon
in the United States to ensure the highest quality and consistency in the finished product. Activation is carefully controlled
to produce a significant volume of both low and high energy pores for effective adsorption of a broad range of high and low
molecular weight organic contaminants. Coal GAC 400 is formulated to comply with all the applicable provisions of the AWWA
Standard for Granular Activated Carbon (B604) and Food Chemicals Codex. This product may also be certified to the requirements
of NSF/ANSI 61 for use in municipal water treatment facilities.

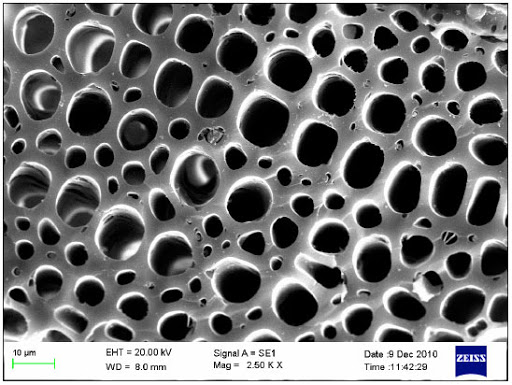
Microscopic pore structure of coal based Activated Carbon.
Individual PFAS have different GAC loading capacities and corresponding breakthrough times (often defined as the number of
bed volumes treated prior to detection in the effluent) (Eschauzier et al. 2012). GAC removal capacity for PFOS is greater
than PFOA, but both can be effectively removed (McCleaf et al. 2017). In general, shorter chain PFAS ( e.g. PFBA perfluorobutanoate)
have lower GAC loading capacities and faster breakthrough times. However, influent concentrations for the shorter chain PFAS
are often an order of magnitude, or more, lower than the longer chain PFAS. For these types of applications where the influent
concentrations for the shorter chain PFAS are much lower and in the low ppt range, GAC can still be a cost-effective sorption
media option that meets applicable regulatory discharge criteria. Figure 12-1 provides an example of removal curves and breakthrough
information for a number of PFAS compounds. Note that all of the PFAS molecules with the exception of the short chain PFBA
are adsorbed and removed down to 70ppt MCL even after 100,000 BV

Specifications Coal GAC 400
Iodine Number 1000 mg/g
Moisture by Weight 2% (max)
Effective Size 0.55 - 0.75 mm
Uniformity Coefficient 1.9 (max)
Abrasion Number 75 (min)
Screen Size by Weight, US Sieve Series
On 12 mesh 5% (max)
Through 40 mesh 4% (max)
Typical Properties Coal GAC 400
Apparent Density 0.54 g/cc
Water Extractables <1%
Non-Wettable <1%
If you have detected PFCs in your water and require removal to below the MCL of 70 ppt, United Manufacturing International
can mobilize Activated Carbon Adsorbers and Coal GAC 400 Activated Carbon to your site. Typical removal efficiencies on our
Coal GAC 400 are down to ND. Send us your operating parameters, concentrations of PFCs, RFQ/RFB and we will provide our professional
proposal to compete for your business. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Wednesday released drinking water
health advisories for four per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances known as PFAS. Those included PFOA, PFOS, PFBS, and GenX.
The Upshot
The EPA 2022 interim health advisories for PFOA (0.004 ppt) and PFOS (0.020 ppt) are orders of magnitude lower than the
2016 health advisories or any state-level enforceable drinking water standards. The new PFOA and PFOS interim health advisories
come in advance of the EPA highly anticipated proposed Maximum Contaminant Level Goals to support the Safe Drinking Water
Act National Primary Drinking Water Regulations for PFOA and PFOS. Those goals will be published later this year. The severely
reduced health advisories beg the question: Can laboratories detect PFOA at 0.004 ppt or PFOS at 0.02 ppt?

Activated Carbon Adsorber Contactors
Back to Home Page
|


